Windows BCDEDIT Command
The Windows BCDEDIT command (Boot Configuration Data Store Editor) sets properties in boot database to control boot loading.
The bcdedit command modifies the boot configuration data store. The boot configuration data store contains boot configuration parameters and controls how the operating system is booted. These parameters were previously in the Boot.ini file (in BIOS-based operating systems) or in the nonvolatile RAM entries (in Extensible Firmware Interface-based operating systems). You can use Bcdedit.exe to add, delete, edit, and append entries in the boot configuration data store.
For detailed command and option information, type
bcdedit.exe /? <command>
For example, to display detailed information about the /createstore command, type:
bcdedit.exe /? /createstor
For an alphabetical list of topics in this help file, run
bcdedit /? TOPICS
Commands that operate on a store
/store Used to specify a BCD store other than the current system default. /createstore Creates a new and empty boot configuration data store. /export Exports the contents of the system store to a file. This file can be used later to restore the state of the system store. /import Restores the state of the system store using a backup file created with the /export command. /sysstore Sets the system store device (only affects EFI systems, does not persist across reboots, and is only used in cases where the system store device is ambiguous).
Commands that operate on entries in a store *
/copy Makes copies of entries in the store. /create Creates new entries in the store. /delete Deletes entries from the store. /mirror Creates mirror of entries in the store.
Run bcdedit /? ID for information about identifiers used by these commands.
Commands that operate on entry options
/deletevalue Deletes entry options from the store. /set Sets entry option values in the store.
Run bcdedit /? TYPES for a list of datatypes used by these commands.
Run bcdedit /? FORMATS for a list of valid data formats.
Commands that control output
/enum Lists entries in the store. /v Command-line option that displays entry identifiers in full, rather than using names for well-known identifiers. Use /v by itself as a command to display entry identifiers in full for the ACTIVE type.
Running “bcdedit” by itself is equivalent to running “bcdedit /enum ACTIVE”.
Commands that control the boot manager
/bootsequence Sets the one-time boot sequence for the boot manager. /default Sets the default entry that the boot manager will use. /displayorder Sets the order in which the boot manager displays the multiboot menu. /timeout Sets the boot manager time-out value. /toolsdisplayorder Sets the order in which the boot manager displays the tools menu.
Commands that control Emergency Management Services for a boot application
/bootems Enables or disables Emergency Management Services for a boot application. /ems Enables or disables Emergency Management Services for an operating system entry. /emssettings Sets the global Emergency Management Services parameters.
Commands that control debugging
/bootdebug Enables or disables boot debugging for a boot application. /dbgsettings Sets the global debugger parameters. /debug Enables or disables kernel debugging for an operating system entry. /hypervisorsettings Sets the hypervisor parameters.
Command that control remote event logging
/eventsettings Sets the global remote event logging parameters. /event Enables or disables remote event logging for an operating system entry.
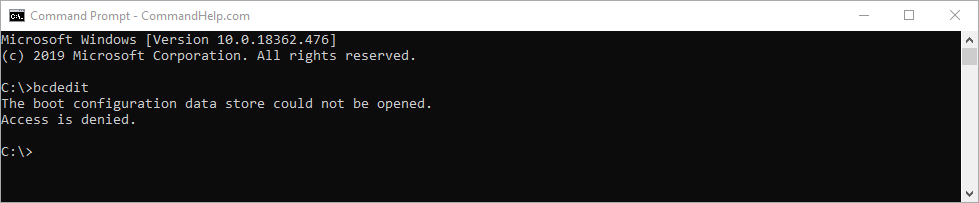
* Note, you must use an elevated command prompt or you will receive the following error: